Award ID: 706 Company: Estudi Bel, Arquitectura i Urbanisme SLP I+D
Allgemeine Informationen
- Datum: 2020-05-18 11:00:47
- Firma: Estudi Bel, Arquitectura i Urbanisme SLP I+D
- Ansprechpartner: Mr. Jaume Bel Homedes
- E-Mail: jb@estudibel.com
- Anschrift: 8, Tortosa
- Telefon/Fax: 616436789 /
- Land: España
Beschreibung:
Manus 2017
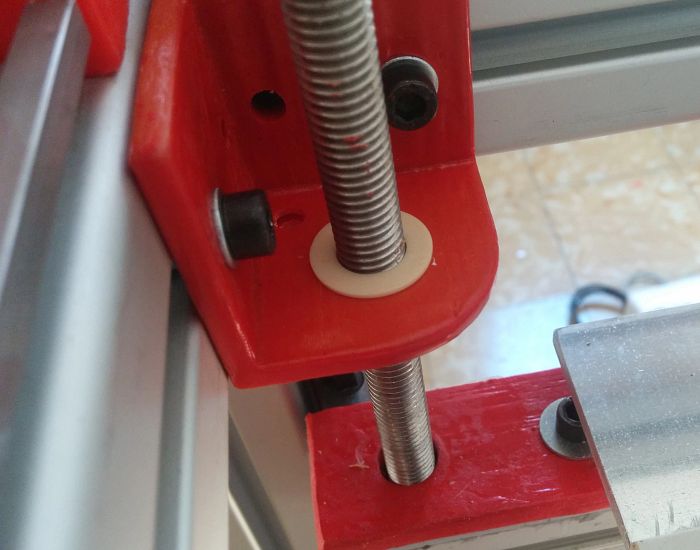
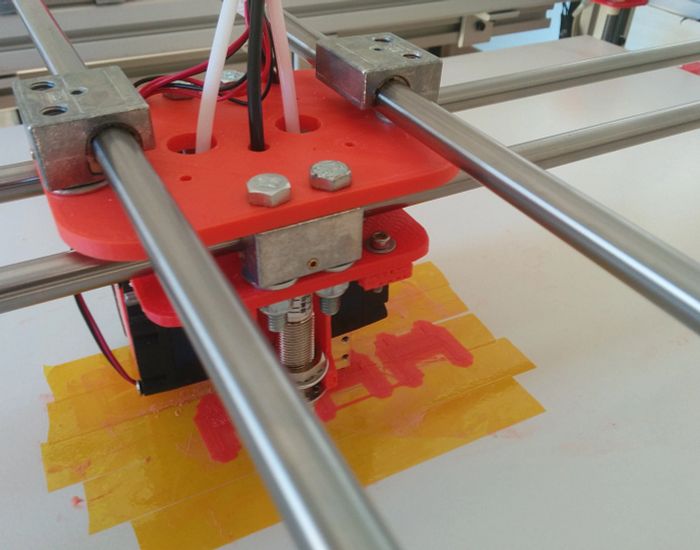
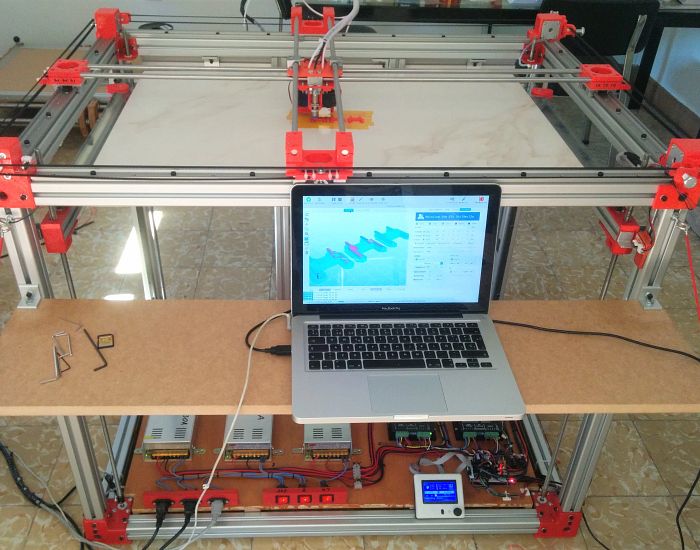
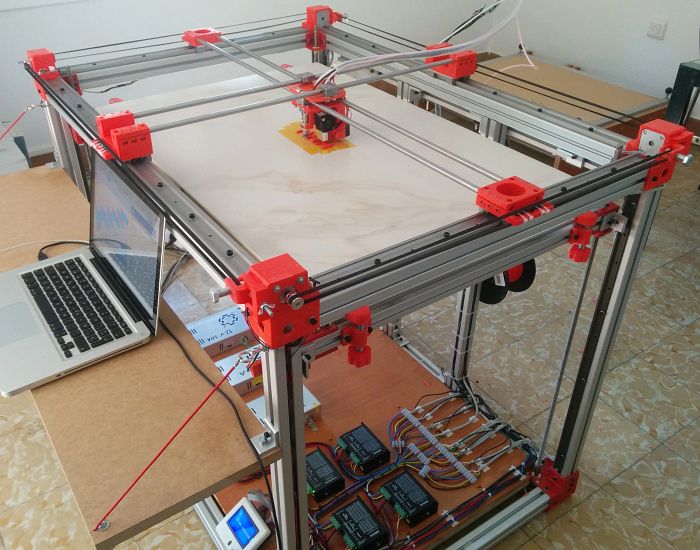
StudiBel 3D 2.0 large-format 800x600x700 cm print volume printer, with high features for experienced users who want to exceed low cost small format. The printer is designed and built entirely with igus® components on all mobile devices. Contains mono-square rail guides on the Z-axis, double-square rail linear guides with four-bearing carriage, plastic bearings in tensioners and bearings, cylindrical and adjustable drylin® bearings in steel axes in the extruder head. It also assembles trapeziodal spindles with two-screw flange nut. (In the current version a threaded rod is used)
StudiBel 3D 2.0 large-format 800x600x700 cm print volume printer, with high features for experienced users who want to exceed low cost small format. The printer is designed and built entirely with igus® components on all mobile devices. Contains mono-square rail guides on the Z-axis, double-square rail linear guides with four-bearing carriage, plastic bearings in tensioners and bearings, cylindrical and adjustable drylin® bearings in steel axes in the extruder head. It also assembles trapeziodal spindles with two-screw flange nut. (In the current version a threaded rod is used)
Problem:
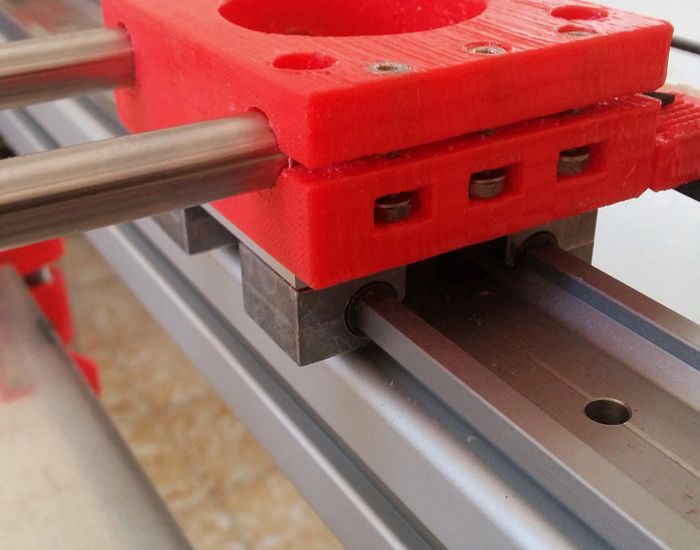
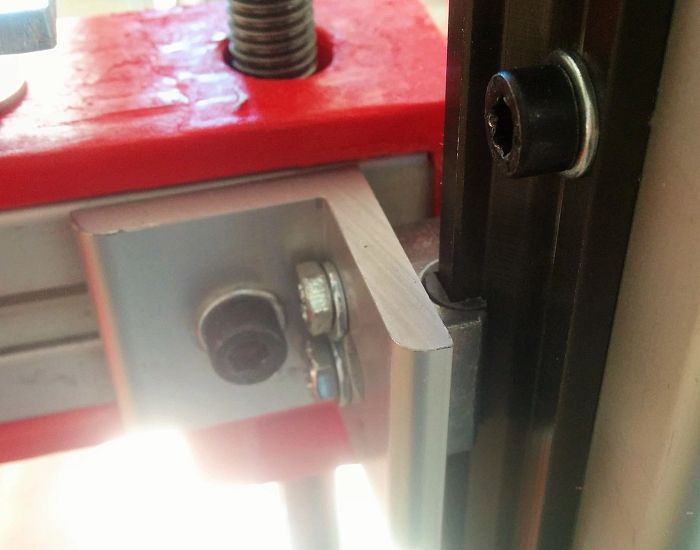
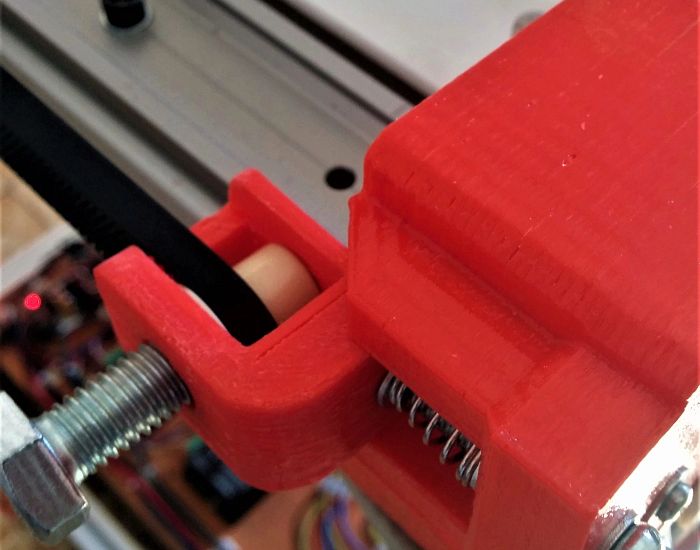
In the second version of the printer that we designed, the StudiBel3D 2.0, our effort was focused on building the XY system as light as possible and moving all the heavy masses out of the moving parts (motors, bars and bearings) to reduce Its inertia to the minimum possible and thus increase the printing speed. The problem resided in the X and Y axes that for large format (1000mm of length of bar) which required heavy extruded profiles of aluminum to reduce the deformation by arrow in the center point, which increased the mass of these axes. We designed a solution of two motors opposed per axes and used two hardened steel bars on each axis, X and Y, but did not manage to reduce the shaft by deformation of the same bars, and also because of the torsion of the anchorage with the linear cylindrical guides where they had to slide. We found the solution in the double guide with square bearing.
Lösungidee:
pThe square bearing asseembled on a double guide provides great resistance to lateral torsion and, therefore, guarantees less deformation by arrow in the central point of the extruder, and allows to use thin bars lighter than the aluminum profile. At the same time, it provides great precision in the slipping, it needs almost null maintenance and it is free of lubrication.
With this design we managed to overcome size limitations of non-industrial user 3D printing at low cost with high precision and great potential, while we combined a more powerful CNC electronics with a 32-bit OpenSource board.
Power, precision and low maintenance available for home users.
With this design we managed to overcome size limitations of non-industrial user 3D printing at low cost with high precision and great potential, while we combined a more powerful CNC electronics with a 32-bit OpenSource board.
Power, precision and low maintenance available for home users.